NHS England hospital datasets#
Last modified: 18 Nov 2025
Benefits of using hospital data for research#
National coverage - all NHS-funded hospital care in England.
Longitudinal coverage - unique patient IDs allow patients to be tracked, enabling e.g. care pathway analysis and re-admissions tracking.
Linkage with other hospital datasets - e.g. Mental Health Services Data Set, enabling analysis across healthcare settings.
Detailed and standardised information - datasets include date of admission, and standardised diagnoses and procedures based on international clinical coding systems.
Summary#
UK LLC holds seven NHS England hospital datasets. The four primary datasets are:
Hospital Episode Statistics (HES) Outpatients, HES Admitted Patient Care, HES Accident & Emergency (retired) and Emergency Care.HES Admitted Patient Care (HESAPC) encompasses three further datasets:
HES Critical Care, HES Augmented Care Periods (retired) and HES Maternity.The datasets in the UK LLC TRE span 1998 onwards.
The datasets do not include all mental health or maternity-specific hospital activity. Much of this information is included in the Mental Health Services Data Set (MHSDS) and the Maternity Services Data Set (MSDS), respectively.
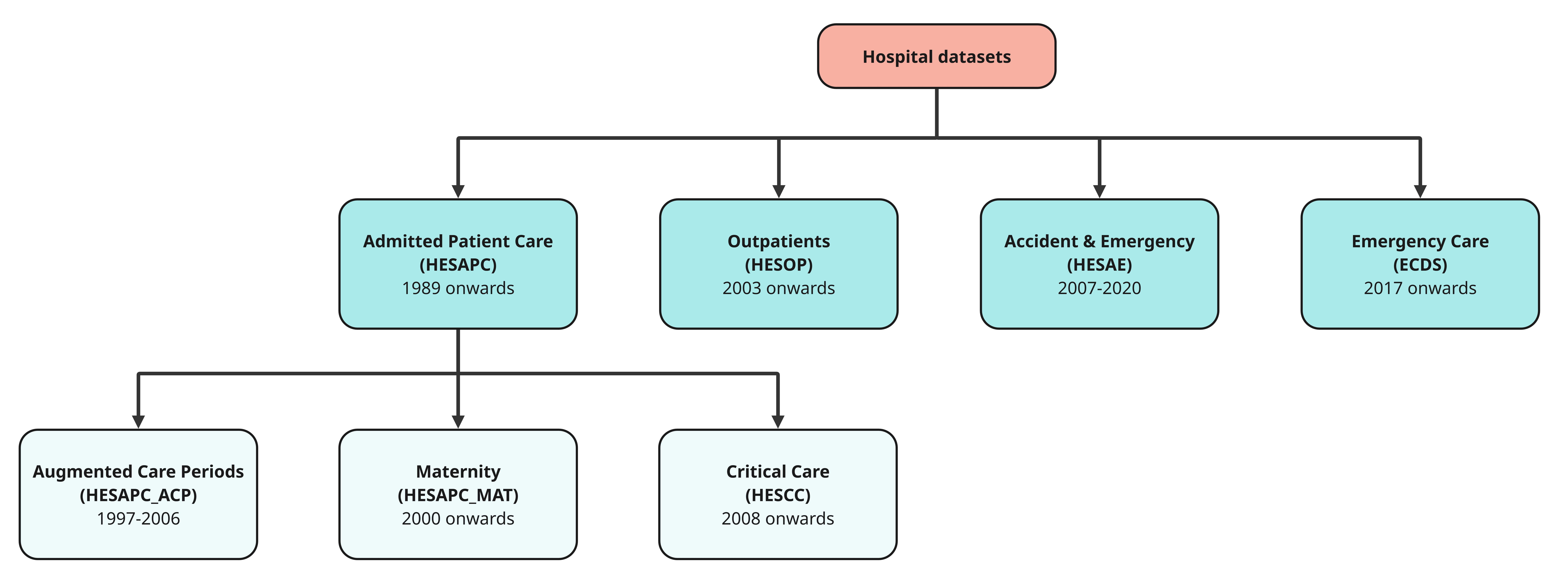
Figure 1 The seven NHS England hospital datasets
For further details see the NHS England monthly provisional and annual reports, HES processing cycle and data quality checks and Processing cycle and ECDS data quality webpages.
Overview of hospital datasets#
For further information see the individual dataset guides.
Table 1 Names, geographical coverage and availability of hospital datasets in the UK LLC TRE (datasets in italics are retired)
Dataset |
Dataset name |
Grouping |
Coverage |
Data available in TRE |
Data owner |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Hospital Episode Statistics (HES) Outpatients |
Hospital |
England |
04/2003 onwards |
NHSE |
|
HES Admitted Patient Care (APC) |
Hospital |
England |
04/1998 onwards |
NHSE |
|
HES APC Augmented Care Periods |
Hospital |
England |
1997 to 2006 |
NHSE |
|
HES APC Maternity |
Hospital |
England |
2000 onwards |
ONS |
|
HES Critical Care |
Hospital |
England |
04/2008 onwards |
NHSE |
|
HES Accident & Emergency |
Hospital |
England |
04/2007 to 12/2020 |
NHSE |
|
Emergency Care Data Set |
Hospital |
England |
10/2017 onwards |
NHSE |
Purpose of data collection#
The datasets were set up for the management and planning of hospital services and for the financial reimbursement to hospitals for the care they have provided to patients. Secondary uses of the hospital datasets, including research, are accommodated within the data collection system as described in the next section.
Processing cycle and frequency of data collection#
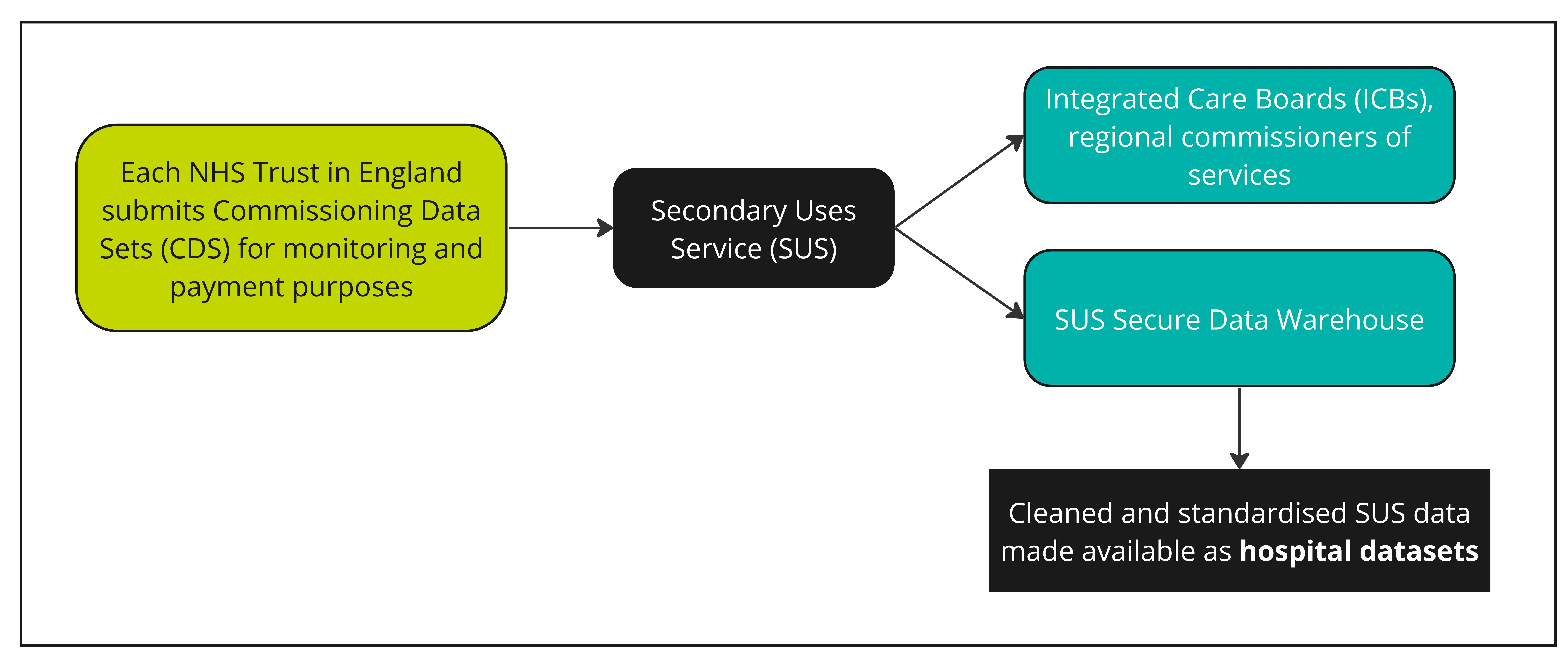
Figure 2 The compilation of the hospital datasets via NHS England’s Secondary Uses Service (SUS)
Stage 1: Collection of the Commissioning Data Sets (CDS)#
The NHS Standard Contract requires all providers of NHS hospital care in England to collect clinical and administrative information as part of the Commissioning Data Sets (CDS). These data are used by regional commissioners of healthcare for NHS patients – Integrated Care Boards (ICBs) – for payment and monitoring purposes.
Stage 2: Submission of the CDS to the Secondary Uses Service (SUS)#
NHS secondary care providers electronically submit their CDS to the Secondary Uses Service (SUS), a national data warehouse located within NHS England. Data from the SUS are made available to the ICBs who use the data to pay hospitals for the care they delivered. These same data can also be processed and used for non-clinical purposes, such as research. Data for these purposes are stored in the SUS Secure Data Warehouse. \
Stage 3: Extraction of hospital datasets from the SUS Secure Data Warehouse#
On a monthly basis, NHS England takes a provisional extract from the SUS Secure Data Warehouse and carries out basic data checks and cleaning, adds geographical fields and attaches pseudonymised patient identifiers (Person_ID) to each episode of care. Each extract is cumulative and contains data submitted for the financial year so far, i.e. month 6 will contain data from April to September. At the end of each financial year, providers have the opportunity to revise and update their submissions for the year via the ‘Annual Refresh’. The finalised hospital datasets are published and made available for research purposes and to NHS England statisticians around September each year.
Further information on how HES data is cleaned is available from NHS England: Automated data cleaning process from SUS into HES.
Equivalent data held across the UK#
Equivalent information about hospital activity across the UK is recorded in the following datasets:
Wales: Outpatients Database for Wales (OPDW), Patient Episode Dataset for Wales (PEDW), Critical Care Dataset (CCDS), Emergency Department Dataset (EDDS) and Intensive Care National Audit and Research Centre (ICNC).
Scotland: Outpatient Appointment (SMR00), Inpatient/daycase activity (SMR01), Maternity interaction/stay (SMR02), Mental health stay (SMR04) and Unscheduled care - A&E.
Northern Ireland: Hospital Inpatient Activity dataset, Hospital Outpatient Activity Dataset, Day case Activity Dataset and A&E Dataset.
